time:Mar 28, 2025 source:ZEXCIT
Vibrating screens are essential in industries such as mining, aggregate processing, and material handling, where they are used for sorting and classifying materials. However, their operation often generates significant noise, which can impact workplace safety, operator comfort, and regulatory compliance.
Excessive noise in vibrating screens is typically caused by factors such as unbalanced forces, loose components, inefficient damping, and resonance effects. Prolonged exposure to high noise levels can lead to hearing damage and reduced efficiency in industrial environments.Reducing noise in vibrating screen operation is crucial for a safer and more comfortable working environment.

Impact Noise:
Material Impact: The primary source, caused by materials hitting the screen deck, screen mesh, and frame. Larger materials and higher feed rates increase impact noise.
Mechanical Impact: From the vibrating mechanism itself, worn parts, or loose connections.
Structural Noise:
Resonance: The screen frame vibrating at its natural frequency, amplifying the noise.
Transmission: Noise transmitted through the supporting structure to the surrounding environment.
Airborne Noise:
Screen Mesh Vibration: The mesh itself can vibrate and generate noise.
Aerodynamic Noise: Air movement caused by the vibrating screen.

A. Material Related Mitigation:
Feed Rate Optimization:
Reduce Feed Rate: The most straightforward solution. Optimizing the feed rate minimizes the amount of material impacting the screen surface at any given time.
Consistent Feed: Ensure a consistent, even feed to avoid surges that cause excessive impact noise.
Material Cushioning:
Screen Deck Liners: Install impact-absorbing liners made of rubber, polyurethane, or other sound-dampening materials on the screen deck surface. These reduce the impact force when materials hit the deck.
Feed Chute Liners: Line the feed chute with similar materials to cushion the initial impact of the material.
Material Conditioning:
Pre-Screening: Remove oversized material before it reaches the vibrating screen, reducing impact and stress on the screen.
Wet Screening (if applicable): Adding water can significantly reduce dust and noise levels. The water acts as a dampening agent.
B. Equipment and Mechanical Optimization:
Vibrator Maintenance:
Regular Inspections: Inspect vibrators for wear and tear, loose bolts, and proper lubrication.
Balanced Weights: Ensure the vibrator weights are properly balanced to prevent uneven and excessive vibration.
Bearing Replacement: Replace worn bearings promptly to reduce noise and prevent further damage.
Screen Mesh Selection:
Consider Mesh Material: Some mesh materials (e.g., rubber, polyurethane) are quieter than others (e.g., steel). Consider the application and noise reduction requirements when selecting mesh.
Mesh Tensioning: Properly tensioned mesh minimizes vibration and noise.
Structural Modifications:
Damping Compounds: Apply damping compounds to the screen frame and support structure to reduce vibration.
Reinforcement: Reinforce the screen frame to reduce resonance and vibration.
Isolation Mounts: Use vibration isolation mounts (rubber, spring, or air-filled) to isolate the screen from the supporting structure, preventing noise transmission. These mounts absorb and dampen vibrations.
Enclosures:
Partial Enclosures: A partial enclosure can block direct noise paths and reduce noise levels in the surrounding area. Ensure adequate ventilation.
Full Enclosures: A full enclosure provides the best noise reduction but requires careful design to allow for access and maintenance. Acoustic panels within the enclosure further reduce noise.
Lubrication:
Proper Lubrication: Ensure all moving parts are properly lubricated to reduce friction and noise.

C. Environmental and Operational Controls:
Distance: Increase the distance between workers and the noise source.
Administrative Controls:
Job Rotation: Rotate workers to reduce their exposure time to high noise levels.
Training: Train workers on proper screen operation and maintenance procedures to minimize noise generation.
Hearing Protection: Provide workers with appropriate hearing protection (earplugs or earmuffs) and ensure they are properly fitted and used.
Acoustic Barriers: Place acoustic barriers or screens between the vibrating screen and workers to block noise.
Type of Screen: The specific type of vibrating screen (e.g., circular, linear, flip-flow) will influence the most effective noise reduction strategies.
Material Being Screened: The size, density, and abrasiveness of the material being screened will impact noise levels.
Ambient Noise Levels: Consider the existing noise levels in the surrounding environment when assessing the effectiveness of noise reduction measures.
Noise Level Monitoring: Regularly monitor noise levels using a sound level meter to assess the effectiveness of noise reduction measures and ensure compliance with regulations.
Frequency Analysis: A frequency analysis can help pinpoint the specific frequencies at which the screen is vibrating, allowing for targeted noise reduction efforts.
Key Steps to Implementation:
Conduct a Noise Survey: Identify the loudest areas and specific sources of noise.
Prioritize Noise Reduction Measures: Focus on the most significant noise sources first.
Implement Solutions: Apply the strategies outlined above, starting with the simplest and most cost-effective options.
Evaluate Effectiveness: Monitor noise levels after implementing each measure to assess its impact.
Adjust and Refine: Make adjustments to the noise reduction strategies as needed to achieve the desired results.
Maintain Equipment: Regular maintenance is essential for sustaining noise reduction benefits.
By systematically addressing the various sources of noise and implementing appropriate mitigation strategies, you can significantly reduce noise levels in vibrating screen operation and create a safer and healthier working environment. Consult with experienced engineers and noise control specialists for more complex situations or if you require specialized solutions.
What is the impact of vibrating screen exciter on screening efficiency
What are the maintenance tips for vibrating screens?
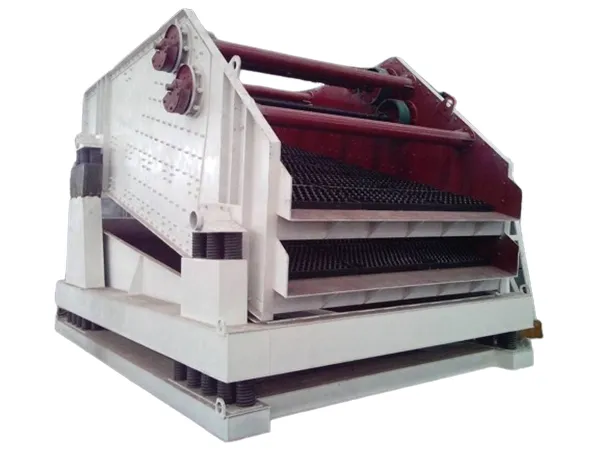

ZSK eccentrics series linear vibrating screen is a new and efficient universal screening equipment, screen box trajectory which is approximately a straight line. This series of screen machine embodies most of the advantages of a biaxial linear screen, with the most extensive scope and application prospects.
READ MORE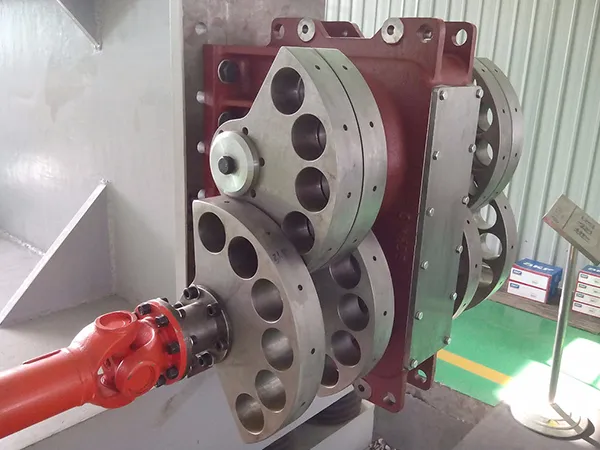
The DF Series Vibrator refers to a range of specialized vibrators used in various industrial applications to generate controlled vibrations. These vibrators are designed for reliability, durability, and efficiency, making them suitable for integration into equipment such as vibrating screens, feeders, conveyors, compactors, and sieves.
READ MORE
A flip flop vibrating screen is a type of vibrating screen that utilizes the principle of elasticity to effectively screen and separate fine materials. This unique design creates a flip-flop motion during the screening process, which helps prevent material blinding and pegging.
READ MORECopyright © 2023 Xinxiang Zongyuan Machinery Equipment Co., Ltd. | All Rights Reserved.